Dexamethasone Intracanalicular Insert for Episodic DED
Early clinical trial results suggest 2–3 weeks of sustained and tapering corticosteroid therapy possible. Howard Larkin reports from the 2022 ASCRS Annual Meeting.

Howard Larkin
Published: Friday, August 5, 2022
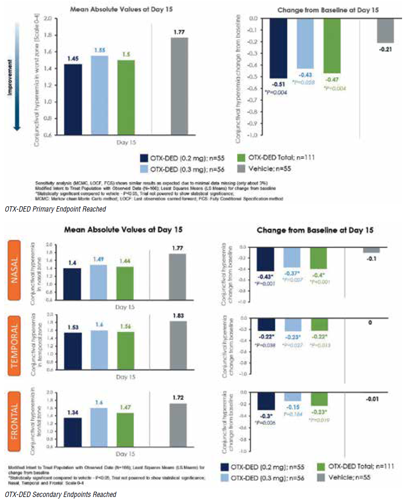
In a phase II clinical study, two strengths of a hydrogel dexamethasone insert for episodic dry eye disease reached the study’s primary endpoint - reducing bulbar conjunctival hyperaemia in the worst ocular zone compared with vehicle 15 days after insertion.
Both the 0.2 mg and 0.3 mg doses of OTX-DED (Ocular Therapeutix) also reduced overall hyperaemia scores. No serious ocular adverse events were reported among the 111 treated and 55 control patients, said Lisa Nijm MD, JD.
Consisting of a biodegradable polyethylene glycol hydrogel delivery platform and dexamethasone, OTX-DED is designed to deliver two to three weeks of sustained tapering therapy, Dr Nijm said. Inserted into the punctum, OTX-DED uses two common strategies to reduce dry eye - primarily through anti-inflammatory therapy and potentially by preserving tears through punctal occlusion. The insert may help avoid potential overuse or misuse of steroid eyedrops, which can lead to intraocular pressure (IOP) elevation and cataract formation, she added.
Though the study was not powered to show statistical significance, the change from baseline in worst-zone conjunctival hyperaemia reached significance against vehicle control in both strengths individually and combined, Dr Nijm said. A sensitivity analysis yielded similar results. Similarly, hyperaemia grade scores improved more in the treatment group than the control group for the total, nasal, temporal, and frontal zones, reaching statistical significance in all except the frontal zone for the 0.3 mg dose.
The symptom endpoint - eye dryness scores using the visual analogue scale - improved in both treatment groups and the vehicle control group. The differences were not statistically significant. However, a post-hoc analysis identified opportunities to differentiate the treatment and control group by developing an appropriate vehicle comparator, Dr Nijm said.
The most common ocular adverse events were epiphora/ lacrimation (8.1% in the treatment groups and 3.6% in the control) and IOP elevation (3.6% in the treatment groups and 0% in the control group). Ocular pain, discomfort, and irritation rates were low in all groups.
Lisa Nijm MD, JD is a corneal and cataract and refractive surgeon at Warrenville Eyecare and LASIK, Warrenville, Illinois, USA, assistant clinical professor of ophthalmology at the University of Illinois Eye and Ear Infirmary in Chicago, and founder of RealWorldOphthalmology.com.
LNijm@RealWorldOphthalmology.com
Latest Articles
Towards a Unified IOL Classification
The new IOL functional classification needs a strong and unified effort from surgeons, societies, and industry.
The 5 Ws of Post-Presbyopic IOL Enhancement
Fine-tuning refractive outcomes to meet patient expectations.
AI Shows Promise for Meibography Grading
Study demonstrates accuracy in detecting abnormalities and subtle changes in meibomian glands.
Are There Differences Between Male and Female Eyes?
TOGA Session panel underlined the need for more studies on gender differences.
Simulating Laser Vision Correction Outcomes
Individualised planning models could reduce ectasia risk and improve outcomes.
Need to Know: Aberrations, Aberrometry, and Aberropia
Understanding the nomenclature and techniques.
When Is It Time to Remove a Phakic IOL?
Close monitoring of endothelial cell loss in phakic IOL patients and timely explantation may avoid surgical complications.
Delivering Uncompromising Cataract Care
Expert panel considers tips and tricks for cataracts and compromised corneas.
Organising for Success
Professional and personal goals drive practice ownership and operational choices.