IOL, Cataract, Refractive
Advances in Toric IOL Alignment
Biomorphometric approaches offer high precision and increase efficiency.

Cheryl Guttman Krader
Published: Friday, March 1, 2024
A prospective clinical study evaluating two biomorphometric systems for intraoperative guidance of toric IOL positioning show both were associated with very low misalignment, said H Burkhard Dick MD, PhD.
“Cataract surgeons agree that the future will be digital and biomorphometric decision-making will play a major, if not a decisive, role in our procedures,” he said. “Compared to manual marking of the reference axis, biomorphometric-guided alignment techniques definitely improve surgical workflow and appear to be a step towards achieving higher patient satisfaction after cataract surgery. Other companies have also introduced biomorphometric approaches for toric IOL alignment that take us away from reliance on preoperatively marking the reference axis.”
The study included 28 eyes of 23 patients who underwent cataract surgery performed by a single surgeon with implantation of a single type of toric IOL.1 Mean preoperative cylinder for the group was about 2.2 D.
The study was designed to compare the performance of two commercially available biomorphometric methods for toric IOL alignment—an image-guided system (CALLISTO eye Z ALIGN, Zeiss) in which the reference and target axes are superimposed into the surgical microscope while scleral and limbal blood vessels are matched with a preoperatively captured image, and a femtosecond laser-assisted capsular marking system (IntelliAxis-L, Lensar) that creates markings on the capsule during capsulotomy and compensates for cyclorotation by matching a preoperatively captured iris image with the intraoperative image through iris registration.
“Both systems compensate for cyclorotation that can occur when patients change from an upright position,” Dr Dick said.
The two systems were applied simultaneously in each case. The final toric IOL alignment was guided by the capsular markings. Misalignment from intended axis was analysed as the study outcome and determined based on analysis of images from an intraoperative surgical video and postoperative slit lamp images.
The results showed mean misalignment was very low with both methods, but it was significantly less using the capsular marking system compared to the digital marking approach (1.71° versus 2.64°; P = 0.016). The greater precision of the femtosecond laser-assisted method may be attributed to its potential to avoid parallax error, which is partly explained by the fact the alignment marks made with the laser are approximately the same level as the toric IOL, Dr Dick explained.
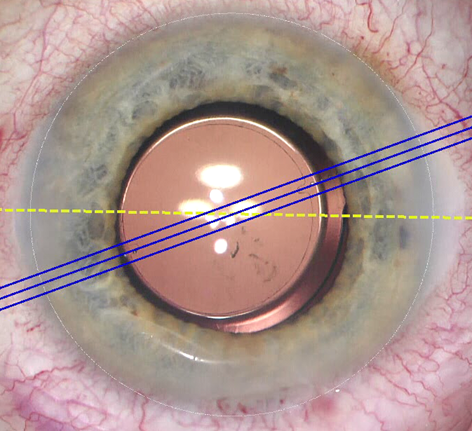
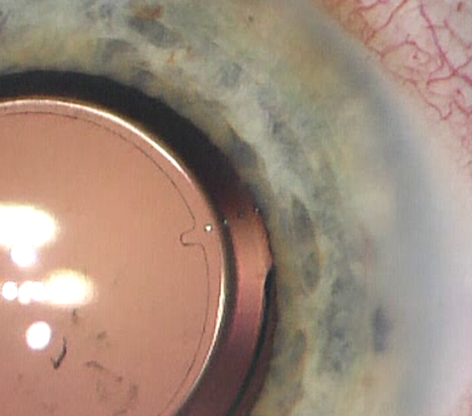
Refractive and functional outcomes were excellent. Mean postoperative uncorrected distance visual acuity was 0.14 logMAR, and mean postoperative refractive astigmatism was 0.3 D.
“Our study was not designed to compare refractive and visual acuity results associated with the two methods, and it is questionable whether the lower probability of misalignment with the capsular marking approach would have led to significant differences,” Dr Dick said.
He noted that previous studies have shown the superiority of the femtosecond laser-assisted and digital marking methods of toric IOL alignment with manual marking.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study that compared two biomorphometric methods for toric IOL alignment.”
Dr Dick spoke at the ESCRS Symposium during Refractive Surgery Subspecialty Day at AAO 2023 in San Francisco, US.
1. Schultz T, Hoffmann S, Dick HB. “Comparison of toric intraocular lens alignment between femtosecond laser-assisted capsular marking and digital marking,” J Cataract Refract Surg. 2023; Oct 17. Epub ahead of print.
H Burkhard Dick MD, PhD is Professor and Chairman, Department of Ophthalmology, Ruhr University, Bochum, Germany. burkhard.dick@kk-bochum.de
Latest Articles
Towards a Unified IOL Classification
The new IOL functional classification needs a strong and unified effort from surgeons, societies, and industry.
Organising for Success
Professional and personal goals drive practice ownership and operational choices.
Update on Astigmatism Analysis
Is Frugal Innovation Possible in Ophthalmology?
Improving access through financially and environmentally sustainable innovation.
iNovation Innovators Den Boosts Eye Care Pioneers
New ideas and industry, colleague, and funding contacts among the benefits.
José Güell: Trends in Cornea Treatment
Endothelial damage, cellular treatments, human tissue, and infections are key concerns on the horizon.
Making IOLs a More Personal Choice
Surgeons may prefer some IOLs for their patients, but what about for themselves?
Need to Know: Higher-Order Aberrations and Polynomials
This first instalment in a tutorial series will discuss more on the measurement and clinical implications of HOAs.
Never Go In Blind
Novel ophthalmic block simulator promises higher rates of confidence and competence in trainees.